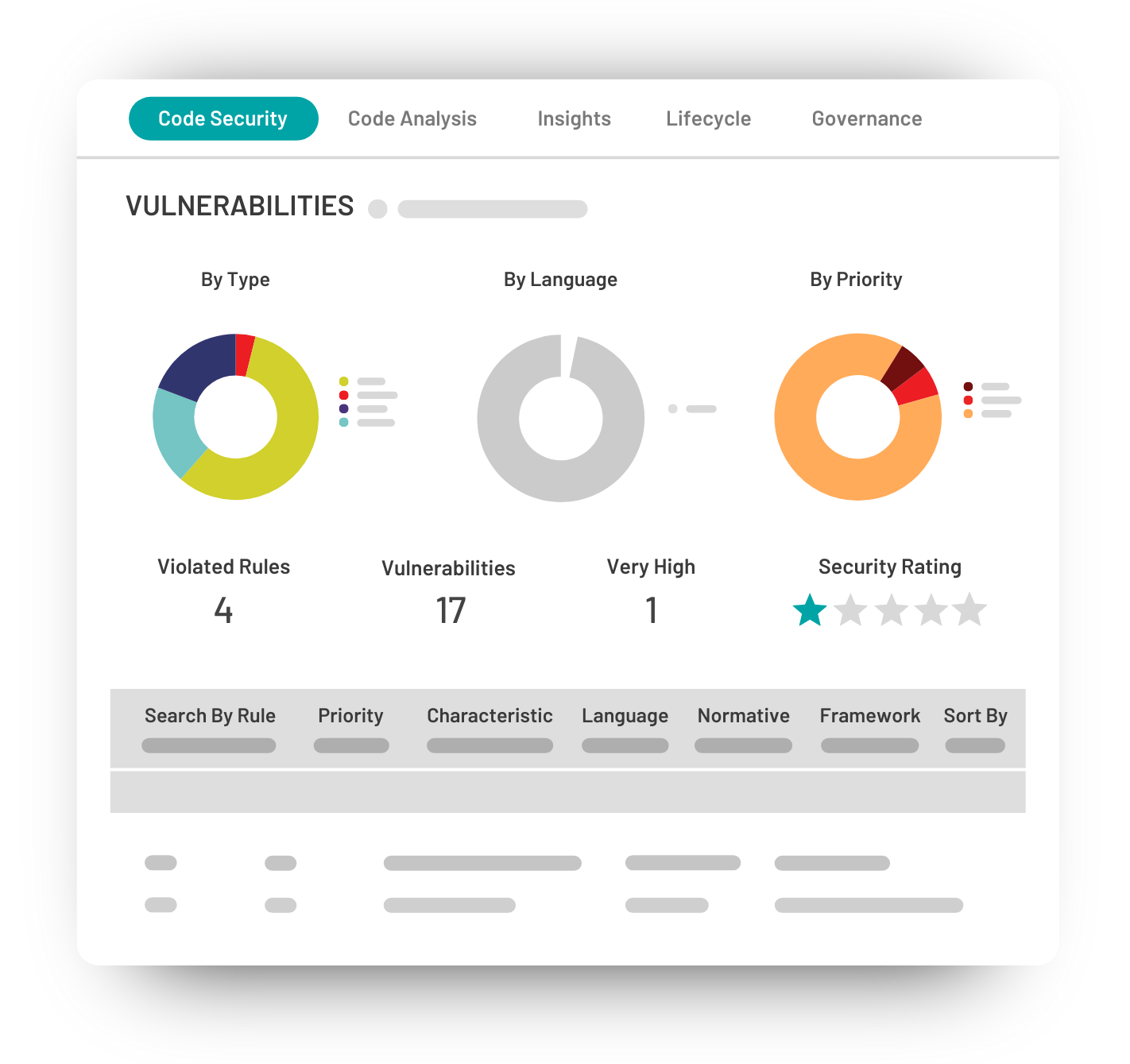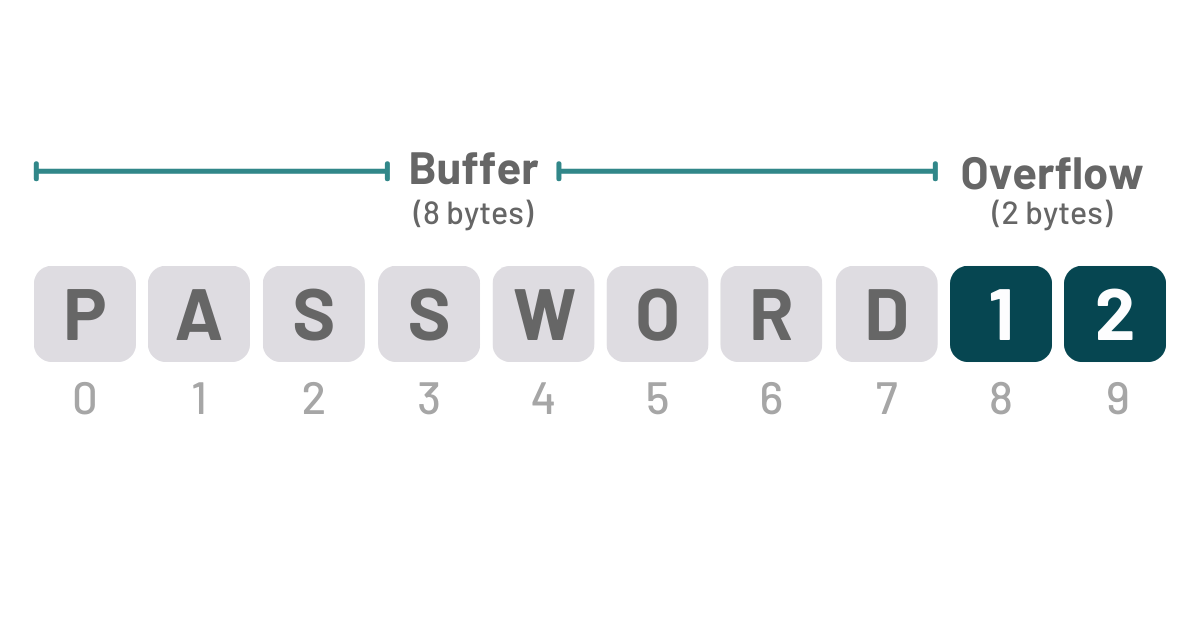
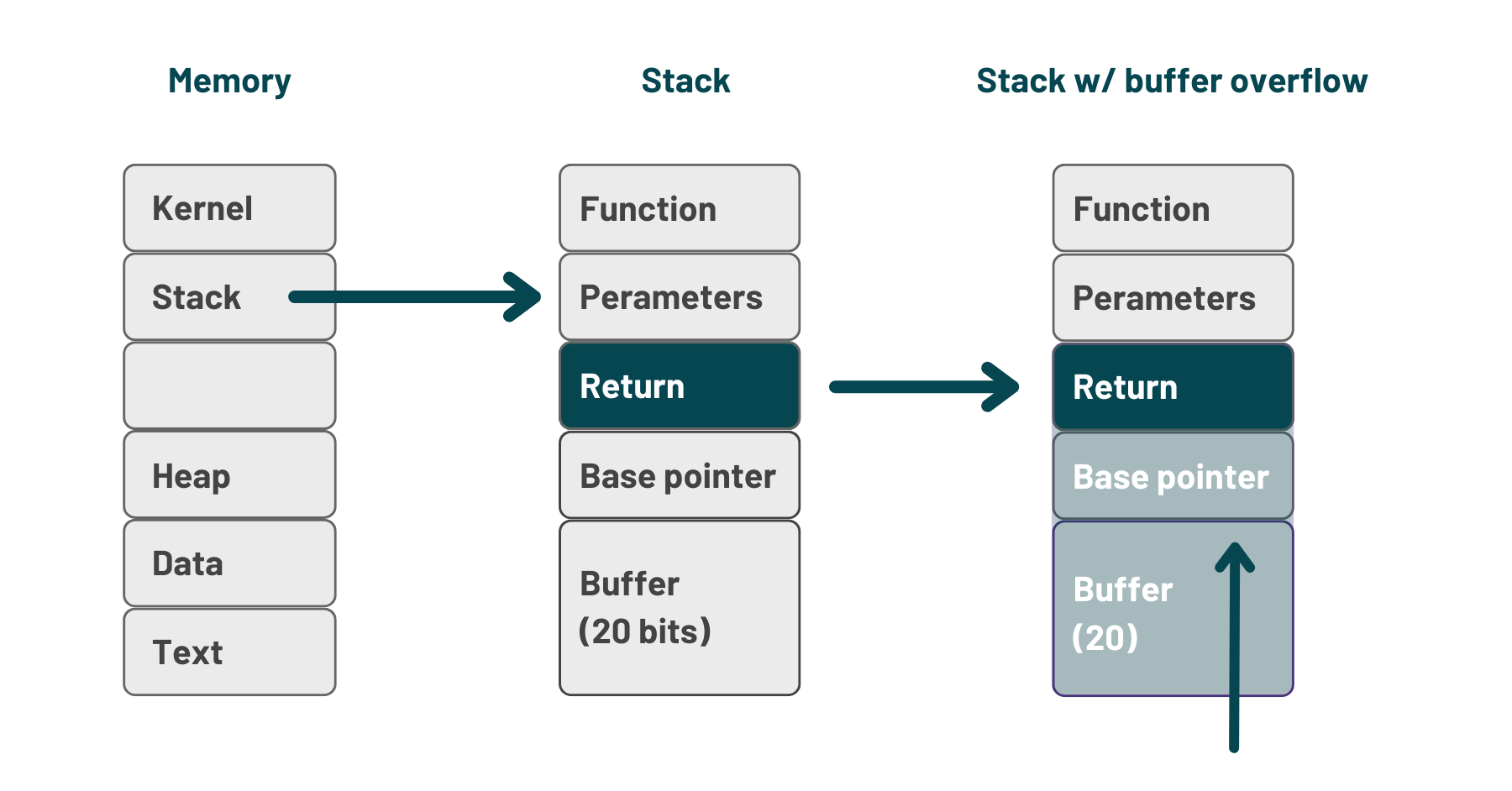

According to OWASP Top 10, XSS is the second-most prevalent issue found in the majority of web applications. By using XSS, attackers can bypass the Same Origin Policy (SOP) in a vulnerable application by entering malicious code that is mistakenly interpreted as user input. This can be done with technologies like VBScript, ActiveX, Flash, and even CSS, but JavaScript attacks are the most common.
XSS differs from SQL because it does not target the database of web applications; it mostly limits itself to their front end.
These attacks can be non-persistent, persistent, and DOM-based. The consequences of XSS attacks can be very damaging, especially when combined with social engineering.
Websites or web interfaces can become corrupted and unsafe. Cookies and authentication information can be stolen, leading to identity theft. By hacking a vulnerable company website, attackers can gain control of the company’s computer clients.